oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo

o

BSL Version
o
- The cosmic microwave background can help scientists piece together the history of the universe.
o
o
o

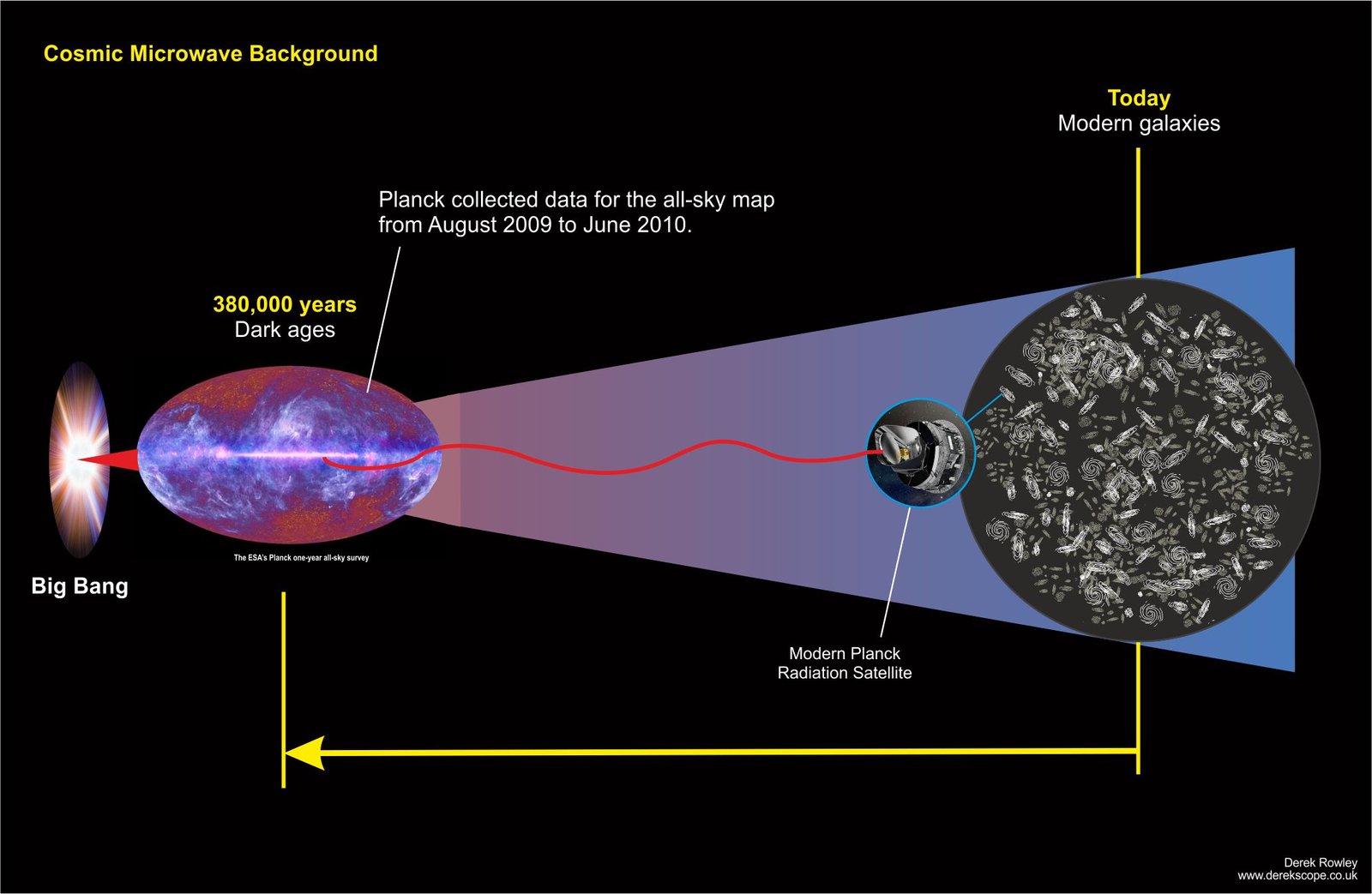
- Modern Planck Radiation Satellite
Planck collected data for the all-sky map from August 2009 to June 2010.
o - The satellite is the most sensitive telescope ever designed to study the cosmic microwave background.
o - The remnants of radiation from the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago – Planck’s detectors by microwave radiation to measure the temperature of this light, searching for regions that are slightly warmer or colder than the average.
o
oooo
The dawn of the Universe (Dark ages)
oooo
- This all-sky image of the cosmic microwave background, created from data collected by the European Space Agency’s Planck satellite’s first all-sky survey, shows echoes of the Big Bang left over from the dawn of the universe.
o
o
o
o
o
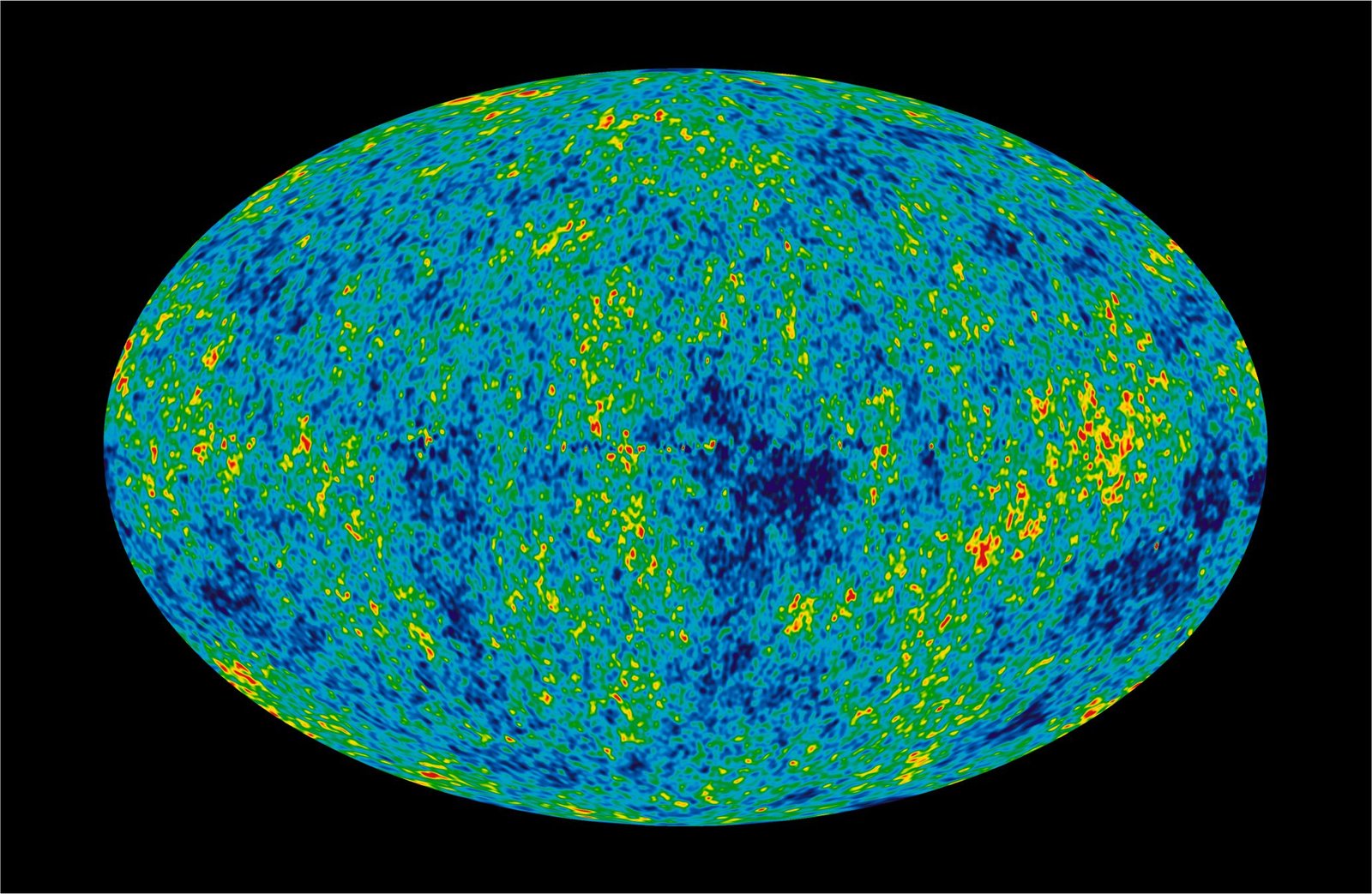
Comparison of Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB)
results from COBE, WMAP and Planck.
oooo

- First imgine – The map of the CMB anisotropy formed from data taken by the COBE spacecraft.
o
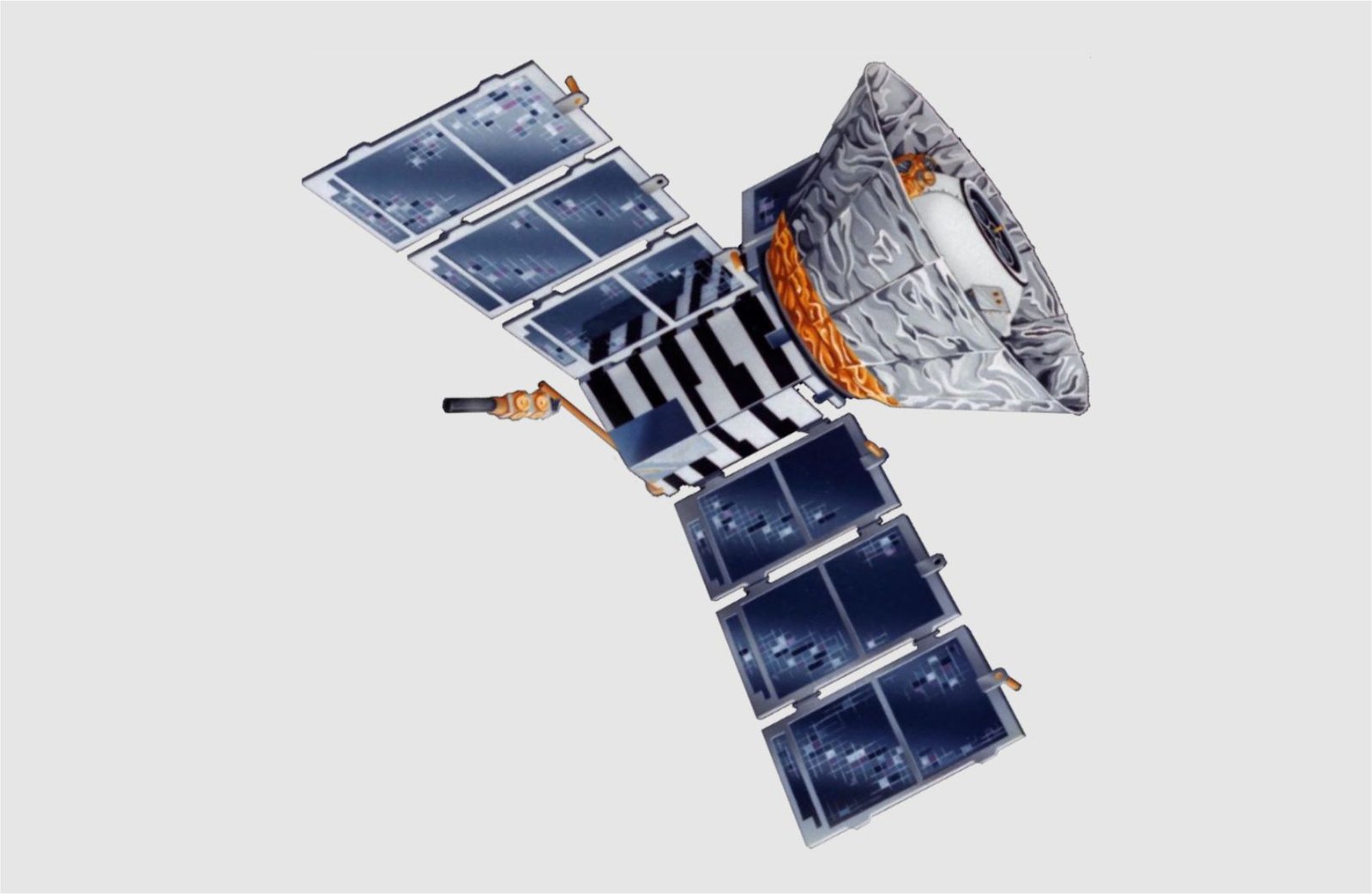

- 1989 to 1993 COBE
Cosmic Background Explorer (CMB) / Spacecraft Explorer 66
(Wikipedia)
- One-year WMAP image of background cosmic radiation (2003).
o
o


- August 2009 to June 2010 image of modern background cosmic radiation.
o

- 2009 to 2013 Planck
COBRAS / SAMBA Space telescope
(Website: ESA Planck)
(Wikipedia)
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
oooo
Back to The Universe / next to Objects page.